Keyword [Classification] [Image Reconstruction] [CapsulesNet]
Sabour S, Frosst N, Hinton G E. Dynamic routing between capsules[C]//Advances in neural information processing systems. 2017: 3856-3866.
1. Overview
基于认知神经科学领域中芒卡斯尔(V.B. Mountcastle)发现的大脑皮层功能柱结构(功能柱-微柱),论文提出capsule概念。
1.1. Capsule定义
- Capsule是一组神经元,其activity vector表示一个特定实体(entity)类型(object or object part)的实例化参数(instantiation parameters).
- Activity vector的长度表示entity存在的概率,方向表示instaniation parameters.
- Instantiation parameters includes pose (position, size, orientation), deformation, velocity (速度), albedo (反照率), hue, texture etc.
1.2. Capsule机制
L level的activity $capsule_i$ 通过transformation matrices predict L+1 level $capsules_j$的instantiation parameters.
当多个predictions agree, L+1层中某个$capsule_j$ become active. (即高层$capsule_j$代表了低层$capsule_i$的组合,如数字2的多个低层特征由多个$capsule_i$表示,同时满足这些特征时,某个代表这些特征组合的高层$capsule_j$被激活)
在CapsNet中使用了iterative routing-by-agreement机制:对于L+1 level中某个$capsule_j$的 activity vectors ($v_j$)和L level中的一个$capsule_i$对其作出的prediction ($\hat{u_{j|i}}$)而言,两者scalar product ($\hat{u_{j|i}} · v_j$)越大, A越倾向于将其output发送给这个$capsule_j$.
CapsNet在MNIST数据集上优于CNN,最高达到99.75%左右。
2. Introduction
2.1. 假设
- 假设,人类的多层视觉系统会在每个fixation上建立一个类似parse tree的东西。
- 假设,对于一个fixation,parse tree可以通过对一个固定的多层神经网络carve (类似于剪枝)得到。
每层会被划分为多个神经元组(capsule), parse tree中每个node都会对应一个active capsule (即parse tree中每个node代表一层神经网络中的一组神经元,该组神经元可称为capsule).
通过iterative routing机制,每个active capsule都会选择上一层中的某个capsule作为parent node. 对于higher level视觉系统,iterative routing机制将用于解决物体部分组合到整体的过程。
2.2. 存在性表示方法
- logistic unit.
- length of the vector of instantiation parameters (squashing function, 论文采用).
2.3. Dynamic Routing
- 由于capsule输出的是向量,用dynamic routing机制能够确保capsule的输出send to合适的parent node.
- 对于L level的capsule A和L+1 level的capsule B. A首先计算prediction vector (A的output乘以weight matrix), 然后计算prediction vector与B ouput的scalar product, 反馈给AB之间的coupling coefficient.
- scalar product越大,对AB之间coupling coefficient的反馈越大,即-AB之间的coupling coefficient增加,A与其他parents之间的coupling coefficients减小(softmax function).
2.4. 分割重叠数字
- 由于max pooling的routing机制会忽略local pool中大部分active feature detectors. 而routing by agreement more effective不存在这样的问题,因此能够分割高度重叠的object.
- Max pooling throw away information about the precise position of the entity within the region.
2.5. 相比于CNN的改进
- 使用vector output capsule代替CNN中的scalar output feature detectors.
- 使用routing by agreement代替max pooling.
2.6. Coding
- For low level capsules, location information is place coded by which capsule is active.
- As we ascend the hierarchy more and more of the positional information is rate coded in the real valued components of the output vector of a capsule.
- 从place coding到rate coding表明higher level capsule用更高自由度represent更复杂的entities, 即capsule的维度随着层级的增加而增加。
3. Capsule计算
3.1. Squashing function
(L level $capsule_i$, L+1 level $capsule_j$)
- 使得较短向量长度缩放为0,较长向量长度缩放为1.

$v_j$. capsule_j的输出向量。
$s_j$. $capsule_j$的总输入向量。 即L level中所有$capsule_is$到L+1 level中特定一个$capsule_j$的prediction vector加权和。
3.2. Total input & prediction vectors
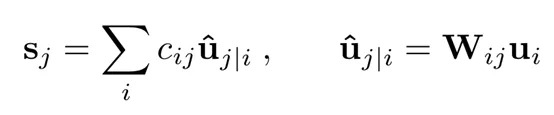
$u_i$. capsule_i的输出向量。
$w_{ij}$. weight matrix.
$u_{j|i}$. prediction value from a $capsule_i$ to a $capsule_j$.
$c_{ij}$. coupling coefficients between a $capsule_i$ and a $capsule_j$.
3.3. Coupling coefficients
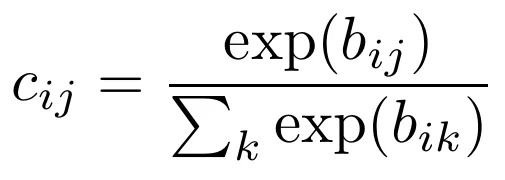
$b_{ij}$. the log priors probabilities that $capsule_i$ should be coupled to $capsule_j$. 由两个capsule (i和j)的location和type决定,而非当前input image决定。
通过测量$v_j$和$u_j|i$之间的agreement迭代refine $c_{ij}$.
3.4. Agreement
This agreement is treated as if it were a log likelihood and is added to the initial logit, $b_{ij}$.
3.5. Algorithm
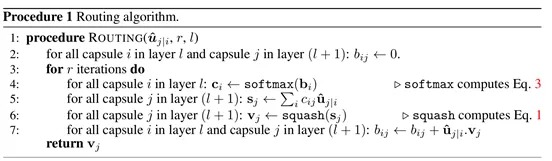
4. Margin Loss
SVM损失函数
- $m^{+}=0.9$, $m^{-}=0.1$
- $T_c=1$, iff a digit present
- suggest $λ=0.5$
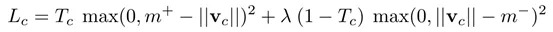
5. CapsNet结构 (Figure 1)
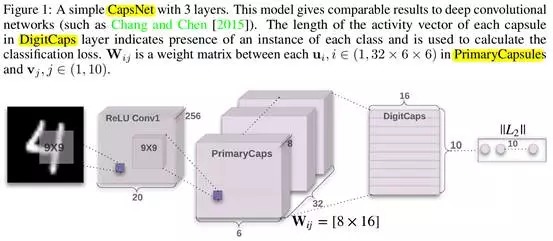
5.1. Conv1
256 kernels, 9x9, 1 stride, ReLu.
- 输入维度 . (batch_size, 1, 28, 28)
- 输出维度. (batch_size, 256, 20, 20)
5.2. PrimaryCapsules
- 输入维度 . (batch_size, 256, 20, 20)
- 输出维度. (batch_size, 32, 6, 6, 8)
激活primary capsule过程可看作是图像render的逆过程。
- PrimaryCapsules is a convolutional capsule layer, 包含32个通道,每个通道含有一个convolutional 8D capsules. 即每个primary capsule包含8个(9x9, 2 stride) conv unit.
- PrimaryCapsule共有(32, 6, 6)个capsule输出,每个输出是一个8维向量。 (6x6) grid中的capsule share weights,与CCN的卷积核原理相同。每个capsule输出a grid of vectors,而不是single vector output.
5.3. DigitCaps
- 输入维度. (batch_size, 3266, 8)
输出维度. (batch_size, 10, 16)
10个16维的capsule.
- CapsNet中,只在PrimaryCapsules和DigitCaps层之间routing. 由于Conv1输出是1D, 不存在orientation to agree on, 因此不在Conv1和PrimaryCapsules层之间routing.
使用Adam optimizer, routing logit $b_ij$初始化为0.
5.4. Reconstruction (Figure 2)

- 输入维度 . (batch_size, 10*16) 或 (batch_size, 16)
输出维度. (batch_size, 28* 28)
Encourage the digit capsules to encode the instantiation parameters of the input digit.
- 在训练阶段,mask除了ground truth对应capsule之外的所有capsule.
- 而测试阶段,mask除了length最大的capsule之外的所有capsule.
目标为最小化sum of squared differences. Reconstruction loss乘以0.0005系数。
To summarize, by using the reconstruction loss as a regularizer, the Capsule Network is able to learn a global linear manifold between a whole object and the pose of the object as a matrix of weights via unsupervised learning.
- As such, the translation invariance is encapsulated in the matrix of weights, and not during neural activity, making the neural network translation equivariance.
- Therefore, we are in some sense, performing a ‘mental rotation and translation’ of the image when it gets multiplied by the global linear manifold.

6. Capsules on MNIST
6.1. 实验结果
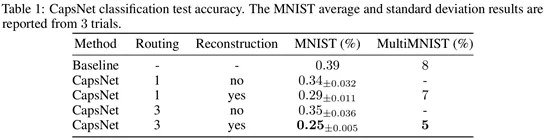
- 使用routing和reconstruction regularizer能够提升性能。
- CNN: 24.56M parameters.
- CapsNet: 11.36M parameters.
6.2. Capsule单个维度代表的意义 (Figure 4)
variations包括厚度、斜度和宽度。16维中几乎总有一维代表数字的宽度,一些维度代表combinations of global variation, 其他一些代表localized part of digit.

6.3. Robustness to Affine Transformations
由于natural variance in skew, rotation, style, etc in hand written digits, 使用CapsNet具有健壮性。
- 训练集 MNIST
digit placed randomly on a black background (平移). - 测试集 affNIST
MNIST digit with a random small affine transformation
CapsNet stop when $train_{acc}=99.23%$, $test_{acc}=79%$.
CNN stop when $train_{acc}=99.22%$, $test_{acc}=66%$.
7. Segmenting Highly Overlapping Digit
7.1. Routing可看做Attention机制
- Dynamic routing可以看做是并行的attention机制,L+1 level的每个capsule都会attend一些L level的activive capsules,忽略其他的。因此,在对象重叠的情况下,也能识别多个对象。
- The routing by agreement should make it possible to use a prior about shape of objects to help segmentation.
- It should obviate the need to make higher level segmentation decisions in the domain of pixels.
7.2. MultiMNIST dataset
- 两张image各方向移动4个pixel,构成36x36 image.
- MultiMNIST result shows that each digit capsule can pick up the style and position from the votes it is receiving from PrimaryCapsules layer.
- 选top 2 length的capsule分别输入decoder中,得到两张digit images.

8. Other Datase
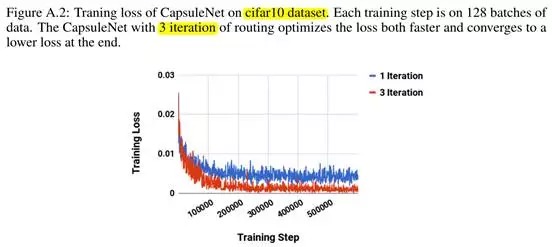
8.1. CIFAR10 (3 channel)
- test_acc: 89.4%.
- drawback 由于CIFAR10 image的背景变化太大,很难model合理大小的网络,导致性能较差。
8.2. smallNORB
- test_acc: 97.3%.
8.3. SVHN
- test_acc: 95.7%.
9. Discussion and previous work
Capsule将pixel intensities转化为vectors of instantiation parameters of recognized fragments, 然后对fragments作transformation matrices, 进而预测 the instantiation parameters of larger fragments.
9.1. CNN不足之处
- Convolutional nets have difficulty in generalizing to novel viewpoints.
- CNN具有translation (平移)不变性,但对于affine transformation (平移、旋转、缩放和斜切)不具有。因此,replicating feature detectors on a grid that grows exponentially with the number of dimensions, 或者指数级增加标注训练集。
9.2. Capsule
- Capsule作了一个非常强的假设:对于image中的each location, a capsule表示至多一个entity的instance.
- Capsule的神经元活动,会随着viewpoint (视角)的变化而变化(同变性equivariance),而不是消除viewpoint带来的影响(如STN网络)。能够同时处理不同object(或object part)上的不同affine transformation.
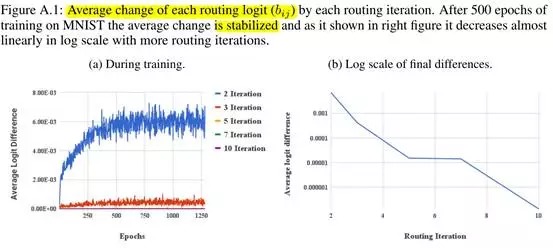
9.3. Routing iteration times